DISTILLATION Part 1
Link for video demonstration on my YouTube platform 👇👇👇
https://youtu.be/pj7oBqjxuIE
https://youtu.be/IPQUpmudvFo
INTRODUCTION
Distillation can be defined as the process of separation of the constituents of a mixture by vaporization and further recovering the liquid at other place by condensation. The feed liquid in distillation apparatus which is to be distilled is called distill and while collected by condensation is called condensate or distillate. Distillation is used to separate volatile components from non volatile components or to separates a mixture of liquids with different boiling points. Distillation is also used to purify liquid mixtures.
Distillation differs from evaporation and drying. In distillation, condensation vapour is required as product while in evaporation the concentrated liquid residue is final product and in drying, solid residue is used as product.
Distillation process involves following apparatus in general:
- Still, in which volatile material is boiled.
- Condenser in which vapors are condensed.
- Receiver in which distillated,i.e. the condensed vapour is collected.
APPLICATION
Distillation is most widely used in pharmaceutical practice. The various application are:
- Distillation method is used for preparation of distilled water.
- Steam distillation is used for separation of volatile oil from vegetable drugs such as cloves and eucalyptus oils.
- Azeotropic distillation is used to get absolute alcohol.
- The process is also used for recovery of solvents from crude drugs extract for the preparation of galencials.
- For purification of organic solvents, distillation is used.
- In petroleum industry using flash distillation method, the crude oil is separated into different fractions.
- Molecular distillation methods are used to purify different organic compounds
- Distillation methods are used to estimate alcohol content in dosage form such as elixirs.
CLASSIFICATION OF DISTILLATION METHODS
These distillation methods are used on laboratory scale as well as on industrial scale
- Simple distillation
- Flash distillation
- Fractional distillation
- Distillation under reduced pressure
- Steam distillation
- Molecular distillation
SIMPLE DISTILLATION OR DIFFERENTIAL DISTILLATION
PRINCIPLE: In this process vapour is removed from the system as soon as it is formed and condensed. Simple distillation is preferred for purification and separation of liquids having volatile. The Rayleigh Equation is useful in the analysis of simple distillation.
Where
L1 and L2 are the total number of moles of the liquid in still before and after distillation
X1 and X2 are the mole fraction of more volatile component in L1 and L2 respectively
x and y are obtained by equilibrium diagram. The plot of x vs 1/y-x is drawn to get integrated value by estimating area under curve between limits x1 and x2
APPARATUS: It consist of distillation flask or still in which liquid which is to be distilled is boiled. A condenser where vapours are condensed into liquid. Water is circulated through the jacket of condenser. The condenser is attached to receiver by adapter. Receiver is used to collect liquid. A thermometer is also inserted into the cork and attached to the flask. The whole unit is made of glass.
WORKING: The liquid is filled into the flask upto one half to two third of its volume. There may be chances of bumping which is avoided by placing small porcelain piece or pumice stone before distillation. The pumice stone should never be added during distillation or in superheated liquid, it may produce sudden splashing. At laboratory scale, the water bath is maintained at the temperature below 1000 C for distilling liquid with boiling point below 800. For inflammable liquids heating mantle are preferred. The liquid starts to boil after some time. At this time the temperature of distillate is observed by thermometer. This temperature is equals to the boiling point of the liquid. As a result vapours start to rise up and pass through condenser. Here vapour is condensed and liquid is collected into the receiver flask. The process is continued.
On large scale still is made of stainless steel or copper. In this case steam is used as heating medium. The steam is circulated into the jacket around the vessel. The thermometer is attached to the still to check temperature of boiling liquid. The still is attached to condenser and to receiver. The metal condenser such as double pipe heat exchangers or tubular heat exchange are used on large scale.
APPLICATION OF SIMPLE DISTILLATION IN PHARMACY:
1. This is used for preparation of distilled water and water for injection
2. This process is used to prepare many volatile oils and aromatic water. For example Spirit of nitrous ether and Aromatic spirit of Ammonia
3. This process is also used to separate non-volatile solid from volatile liquids such as alcohol and ether.
4. Also used for simple concentration of liquid.
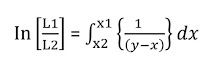





No comments:
Post a Comment